
NIST Cybersecurity Framework Compliance
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework serves as a comprehensive framework for organizations to assess and improve their cybersecurity posture. It offers a structured approach to managing cybersecurity risks, aligning business objectives with appropriate security measures, and enabling effective communication between stakeholders involved in cybersecurity decision-making.
Are you a business striving to enhance your cybersecurity posture and achieve NIST Cybersecurity Framework compliance? We are a leading provider of comprehensive IT solutions designed to help businesses like yours navigate the complex landscape of cybersecurity and align with the rigorous standards set by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
NIST Compliance Consulting
NIST Cybersecurity Framework compliance is more critical than ever in today’s digital landscape, where cyber threats continue to evolve and pose significant risks to organizations of all sizes. By adhering to the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, you can establish a robust cybersecurity program that identifies, protects, detects, responds to, and recovers from potential cyber incidents. This framework provides a proven roadmap for mitigating risks and fortifying your organization’s defenses against cyber threats.
At Empowered IT Solutions, we understand the unique challenges businesses face when it comes to achieving NIST Cybersecurity Framework compliance. Our team of highly skilled cybersecurity experts possesses deep knowledge and extensive experience in helping organizations successfully adopt and implement the framework’s guidelines and best practices. We take a personalized approach, tailoring our solutions to meet your specific needs and industry requirements.
Assessment and Gap Analysis
Our experts will conduct a thorough assessment of your existing cybersecurity measures, identifying gaps and vulnerabilities that need to be addressed to achieve NIST compliance. We analyze your current policies, procedures, technologies, and workforce capabilities to establish a comprehensive baseline.
Customized Roadmap
Based on the assessment results, we develop a customized roadmap that outlines the necessary steps to achieve NIST Cybersecurity Framework compliance. This roadmap takes into account your organization's unique requirements, resources, and risk tolerance, ensuring a practical and achievable approach.
Policy and Procedure Development
We assist you in creating robust policies and procedures that align with the NIST Cybersecurity Framework. Our team ensures that your documentation reflects the best practices outlined by NIST, covering areas such as risk assessment, incident response, access control, and employee awareness training.
Technical Implementation
Empowered IT Solutions helps you implement the technical controls and safeguards necessary to support NIST compliance. From network segmentation and encryption to intrusion detection systems and security monitoring tools, we deploy the right technologies to protect your digital assets effectively.
Ongoing Monitoring and Support
Achieving NIST Cybersecurity Framework compliance is not a one-time effort; it requires continuous monitoring and proactive management. Empowered IT Solutions offers ongoing support, monitoring, and maintenance services to ensure your cybersecurity measures remain effective and up-to-date in the face of evolving threats.
Don’t let cyber threats compromise your business’s success. With Empowered IT Solutions as your trusted partner, achieving NIST Cybersecurity Framework compliance becomes a streamlined and efficient process. Our comprehensive approach, tailored solutions, and deep expertise empower your organization to enhance its cybersecurity posture, safeguard sensitive data, and protect your reputation.
Contact Empowered IT Solutions today, and let our experienced team guide you toward NIST Cybersecurity Framework compliance. Together, we’ll build a secure future for your organization in today’s ever-evolving digital landscape.
The NIST Cyber Security Framework (CSF)
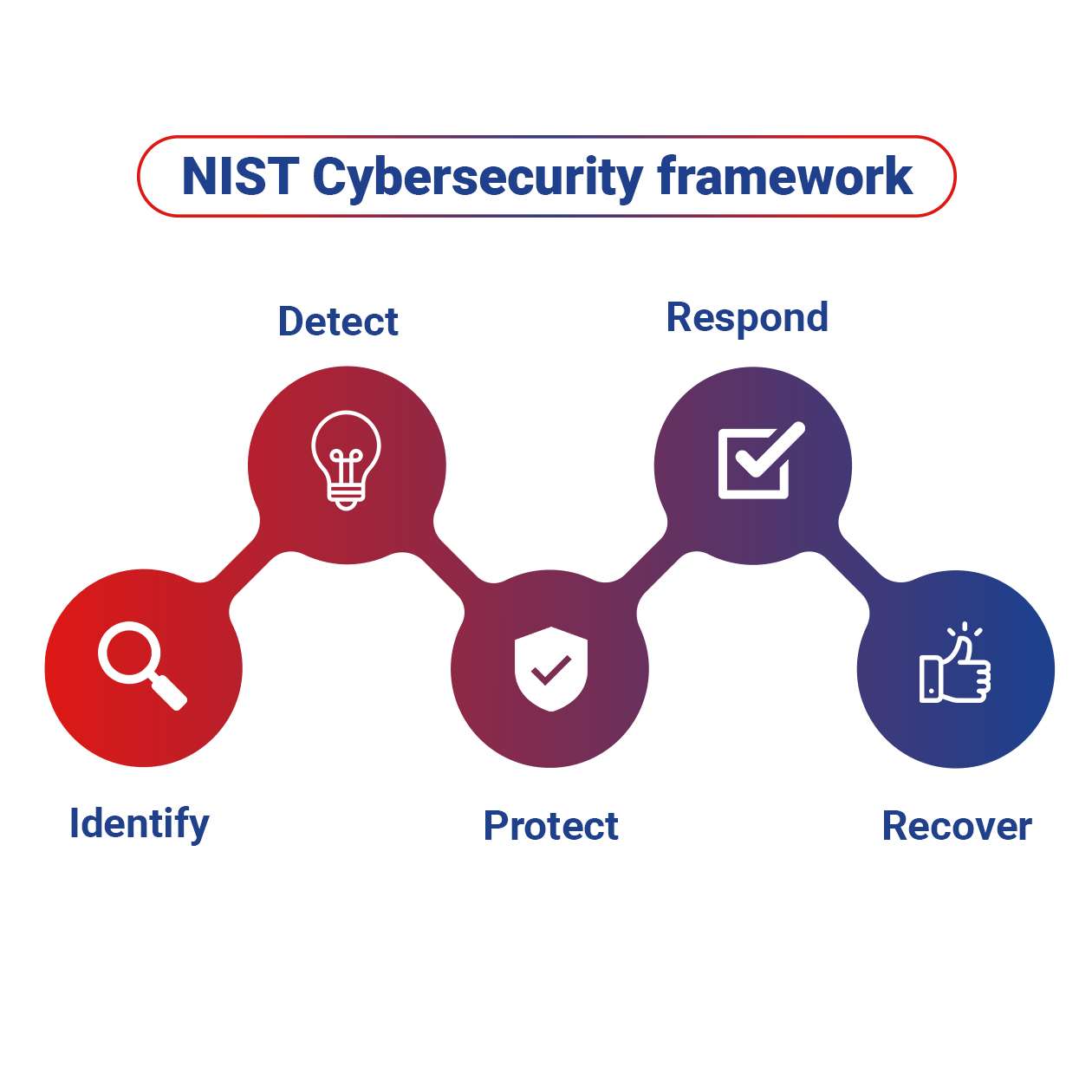
The NIST Cyber Security Framework is designed for individual businesses and other organizations to use to assess the risks they face.
An organization typically starts by using the framework to develop a “current profile” which describes its cybersecurity activities and what outcomes it is achieving. It can then develop a “target profile” or adopt a baseline profile tailored to its sector or type of organization. It can then define steps to switch from its current profile to its target profile.
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework organizes its “core” material into five “functions,” which are subdivided into a total of 23 “categories.” For each category, it defines a number of subcategories of cybersecurity outcomes and security controls, with 108 subcategories in all.
Here are the functions and categories, along with their unique identifiers and definitions:
IDENTIFY
This category helps organizations understand their environment to manage cybersecurity risks to systems, assets, data, and capabilities. It includes asset management, business environment, governance, risk assessment, and risk management strategy.
PROTECT
This category outlines safeguards to ensure the delivery of critical infrastructure services. It includes access control, awareness and training, data security, information protection processes and procedures, maintenance, and protective technology.
DETECT
This category focuses on developing and implementing appropriate activities to identify the occurrence of a cybersecurity event. It includes anomalies and events, security continuous monitoring, and detection processes.
RESPOND
This category involves developing and implementing appropriate activities to take action regarding a detected cybersecurity event. It includes response planning, communications, analysis, mitigation, and improvements.
RECOVER
This category includes activities to maintain plans for resilience and to restore any capabilities or services that were impaired due to a cybersecurity event. It covers recovery planning, improvements, and communications.
Ensure your business meets NIST compliance standards with expert guidance and comprehensive solutions from Empowered IT Solutions. Our team will help you navigate the NIST CSF categories and implement robust cybersecurity practices to protect your assets and data. Contact us today to schedule a NIST compliance assessment and fortify your business against cyber threats.
